Red Tegu: Facts, Diet, Habitat, & Behavior
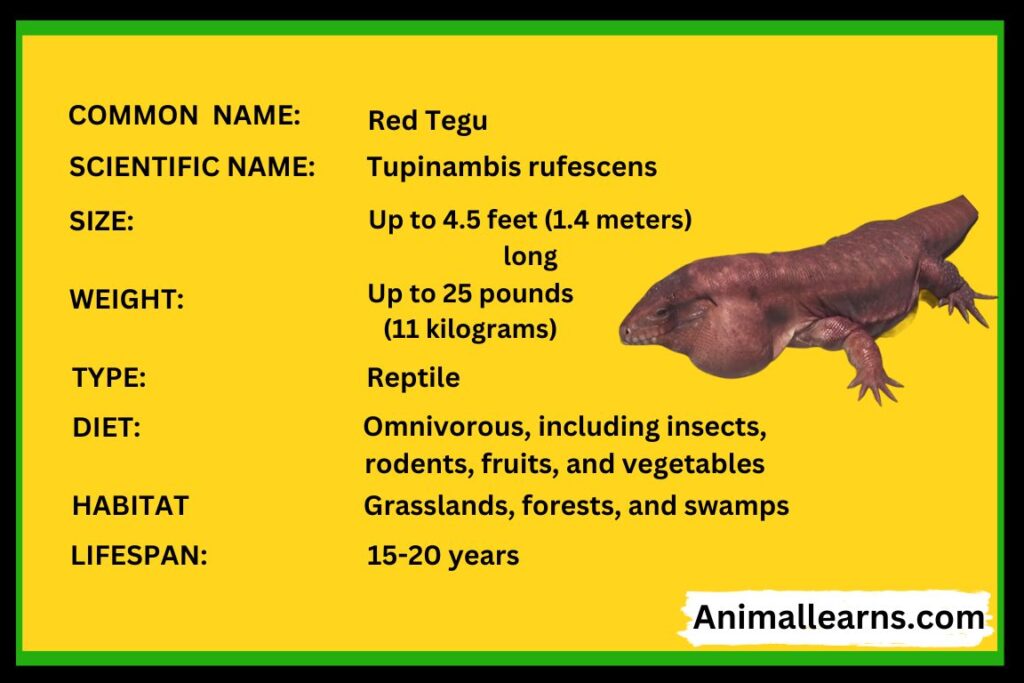
A fascinating species of giant lizard found across South America, especially western Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay, is the Red Tegu. Also called the Argentine Red Tegu Lizard. These reptiles, which are members of the Tupinambis genus, which also contains six other tegu species, are well known for their placid disposition.
With its vibrant red coloration and intelligence, the red lizard is a fascinating reptile like crocodile, snake, tortoise, and turtle. Tegus are big, intelligent lizards that live mostly in South America’s woods and rainforests.
They may even become dogs when they are socialized. They are skilled swimmers and climbers and spend a lot of time searching for other species’ eggs in the ground.
They are friendly creatures, but because of their enormous size and unique care needs, having one requires dedication. Yet, they might be a fascinating option for seasoned reptile lovers looking for the task of taking care of a large reptile, providing a distinctive and fulfilling experience.
Appearance
Contents
- 1 Appearance
- 2 Size and Weight
- 3 Diet
- 4 Reproduction and Life Cycle
- 5 when do tegus hibernate?
- 6 Lifespan
- 7 Habitat
- 8 Behavior
- 9 How to Take Care of Red Tegus
- 10 Feeding
- 11 Keeping Your Red Lizard Healthy
- 12 Are Red Tegus Good Pets?
- 13 Interesting Facts
- 14 How Much Does Red Tegus Cost?
- 15 Are They Friendly?
- 16 Conclusion
- 17 FAQs
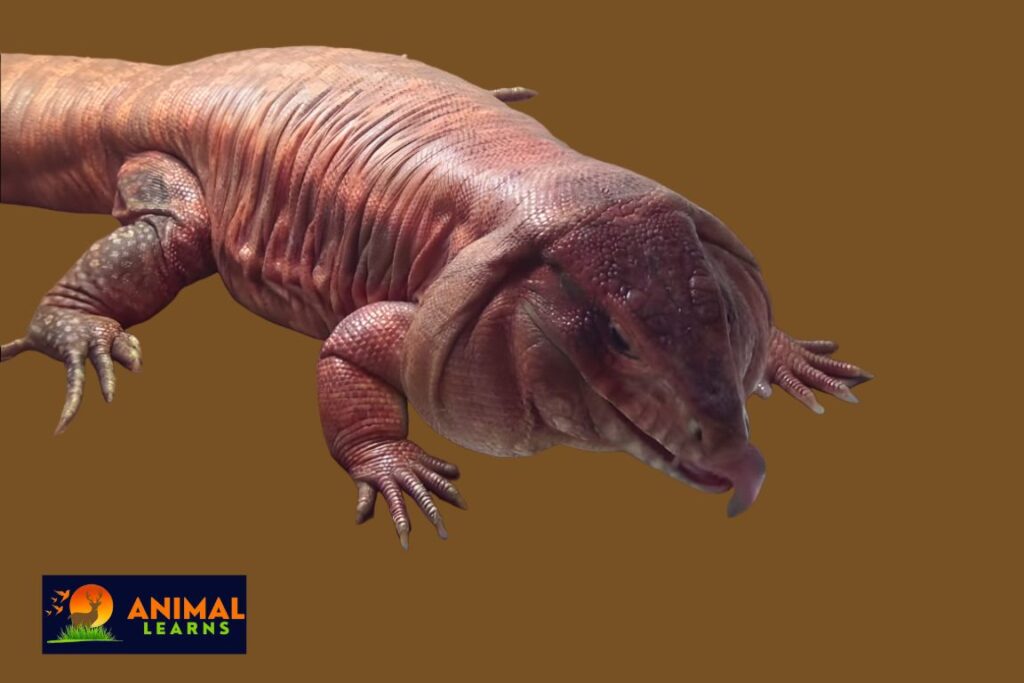

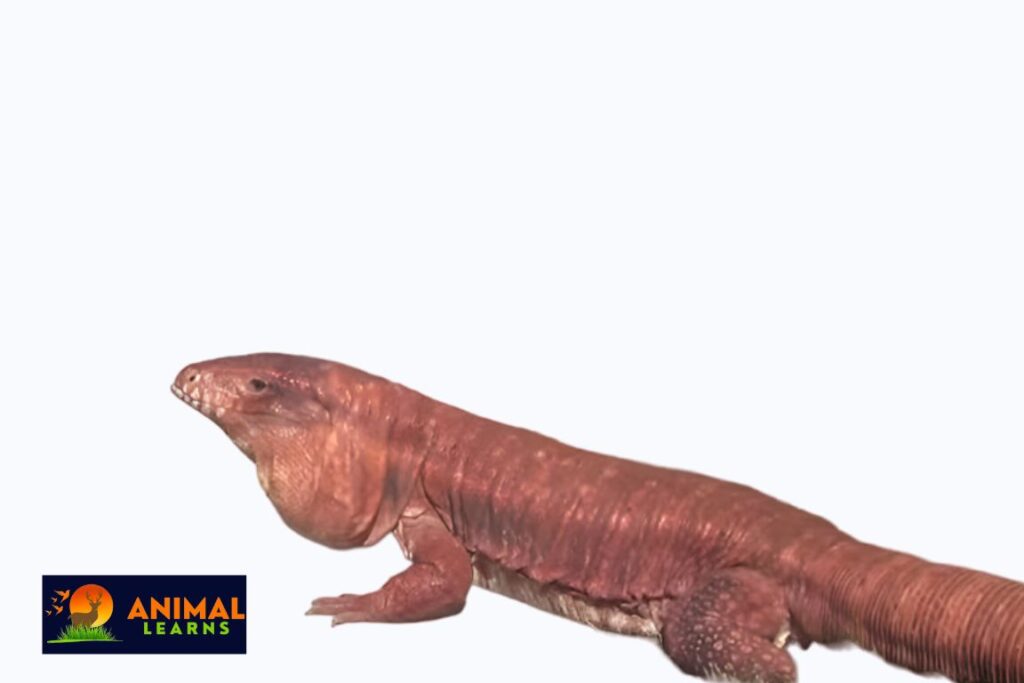
Large lizards known as red tegus have a unique look that varies with age.
Hatchlings
- Brownish-green with black lines running the length of them
- Many shattered white streaks running the length of them
- The red coloring is a little nonexistent.
Juveniles
- Progressively becoming more crimson in color
- Men turn a brighter crimson than women do.
- Adult males may grow up to 140 cm (4.5 ft) in length, while adult females can grow up to 91 cm (3 ft) in length.
- Males also acquire prominent jowls.
Adults
- mostly red in color
- Males have greater vibrancy than females.
- Some individuals have white marks on them.
- The body has strength and muscle.
- A long and prehensile tail that can grip items
- The large and wedge-shaped head
- Huge eyes with yellow irises
- Long and forked tongue
Size and Weight
A tegu may reach a maximum length of 3 feet for females and 3.5 feet for males. Their maximum weight is 25 pounds.
Diet
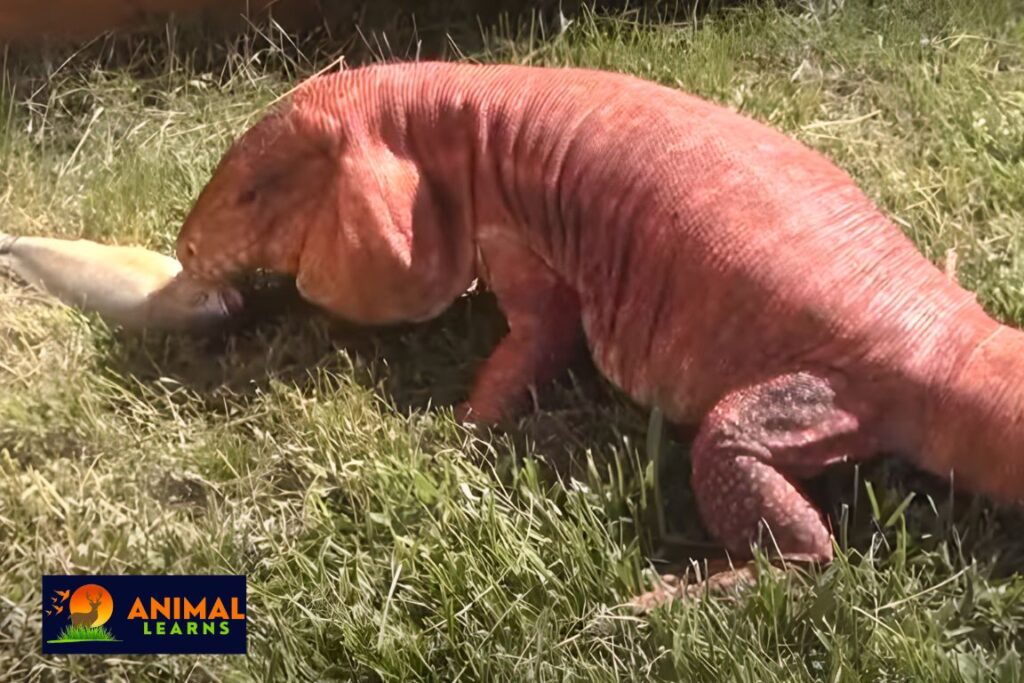

Juveniles and hatchlings require a diet rich in protein that consists of 70–80% invertebrates, including mealworms, roaches, and crickets.
They are also capable of consuming tiny vertebrates like fuzzy rats and pinkie mice. Supplements including fruits and vegetables are OK, but no more than 20–30% of the diet should consist of them.
A more diverse diet consisting of 40–50% fruits and vegetables and 50–60% protein is possible for adult these tegus. Lean meats, eggs, insects, and tiny vertebrates are some of their possible protein sources. They may have leafy greens, squash, berries, and melons among their fruits and vegetables.
| Diet Component | Proportion | Suitable Food Sources |
| Protein | 70-80% for hatchlings and juveniles, 50-60% for adults | Insects (crickets, roaches, earthworms), snails, whole prey (mice, rats, quail), lean ground turkey |
| Plant matter | 20-30% for hatchlings and juveniles, 40-50% for adults | Fruits (chopped or pureed), vegetables (chopped or pureed) |
| Water | Always available | Fresh water |
Reproduction and Life Cycle
They mate before heading into hibernation, with the females then beginning to lay eggs. The process of mating recommences two weeks after they emerge from hibernation and continues thereafter.
In her nest, the mother red-tegu lays anywhere from 12 to 30 leathery eggs. Additionally, they have been seen concealing their eggs within termite mounds. This keeps the eggs at the ideal temperature and provides them with the necessary humidity for growth.
when do tegus hibernate?
Usually, they hibernate from November through March. But the precise date can change according to the tegu’s unique characteristics and the environment. If housed in a warm habitat with steady temperatures, red-tegus in captivity could not hibernate at all.
Lifespan
Given the right care, these lizards may live for 15 to 20 years.
Habitat

Numerous environments, including savannas, marshes, meadows, rainforests, and open fields, are home to these tegus.
| Habitat | Location | Description |
| Tropical rainforests | Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay | Lush forests with abundant food, moisture, and shelter |
| Savannas | Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay | Grasslands with scattered trees and shrubs |
| Deciduous semiarid thorn forests | Argentina | Forests with thorny trees and shrubs |
Behavior
These animals are terrestrial, nocturnal creatures in the wild. In Argentina, where they enjoy a moderate environment, they endure harsh winters where they burrow and become mostly dormant, perhaps for as long as seven months in certain regions.
In addition, they habitually burrow throughout other seasons of the year. They are known to spontaneously hybridize with the Argentine black and white tegu (Salvator merianae) in the ecotone that separates the dry Chaco and the Espinal of central Argentina, creating a stable hybrid zone.
How to Take Care of Red Tegus

Experienced reptile keepers can find great satisfaction in having red tegu as pets. These are huge, intelligent lizards. But for them to flourish in captivity, they need specific attention. The following are some vital tips for caring:
Coverage:
- A large cage that closely resembles, native habitat is required. When they become older, they need a space that is at least 6 feet long, 4 feet wide, and 4 feet tall.
- There should be a temperature gradient in the cage, with a colder end of 75–80°F and a basking region of 100–110°F. To keep these temperatures, use ceramic heat emitters, heat pads, or heat lamps.
- Provide a range of hiding places, such as fake hides, thick branches, and rocks.
- Use a humidifier or often spray the enclosure to keep the humidity between 70 and 80 percent.
- Choose a substrate that is simple to clean and work with, such as coconut coir or cypress mulch.
- To keep an eye on your tegu’s health and take quick care of any possible problems, schedule routine examinations with a knowledgeable veterinarian who specializes in reptiles.
- They are gregarious, intelligent animals that may be consistently and patiently educated.
- At an early age, begin managing your tegu, even only briefly. As you feel more at ease handling your tegu, gradually extend the handling time.
Feeding
Infants and young children should be fed as much as possible in 20 to 30 minutes, either every day or every other day. Adults can eat once or twice a week, roughly enough food to fill a dog dish for five to ten minutes. In addition, feeding schedules vary from season to season since tegus typically burrow from late fall to early winter (2–3 months). You may turn on their lights at this period, and all you have to do is maintain the right humidity levels till they wake up.
Keeping Your Red Lizard Healthy
If you don’t already have an exotic veterinarian in your region, you should locate one before you ever bring your Argentine tegu home. These lizards need specialized treatment that cannot be provided by normal animal clinics or specialists.
Even though your lizard may not need to visit the vet frequently, in the event of an unexpected sickness or issue, you should seek emergency medical attention. Lizards frequently don’t exhibit symptoms of illness until it is fairly advanced.
Are Red Tegus Good Pets?
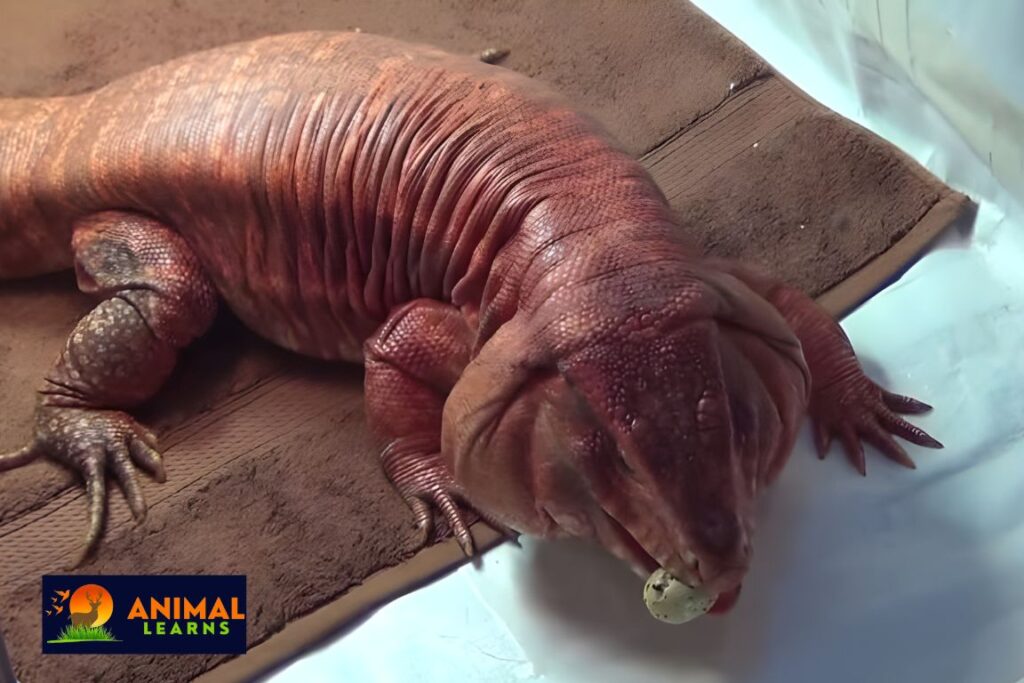

Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay are among the South American countries where they are indigenous. No matter where you reside in the world, these large, tropical creatures require heat since they enjoy hot, muggy conditions.
For the appropriate owners, Argentine tegus may be excellent pets. Given how big these lizards get, it’s critical to understand just how much space they require.
However, don’t let their enormous size scare you away—these lizards are quite calm animals that only need moderate maintenance.
Interesting Facts
- Because of their penchant for eating honey, they are frequently observed demolishing beehives.
- They are known to follow their owners around the home “like a dog” and may be trained to respond to the sound of clickers.
- The color changes as they become older. Egglings are usually brownish-green in color with black stripes, but adults turn a bright red. In general, men have a stronger red color than females.
- Because of their prehensile tails, they can hold onto items. They can climb trees and rocks and catch their prey thanks to this adaptation.
How Much Does Red Tegus Cost?
The price of these reptiles varies from $500 to $2,000 based on several criteria, such as:
Age: Because they are smaller and need less care than adults, hatchlings usually cost less.
Genetics: Tegus with uncommon colorings or desired characteristics, such as severe giantism or high whiteness, can fetch higher prices.
Breeder Reputation: Buying a tegu from a respectable breeder that places a high value on the health and welfare of their animals may cost more, but it guarantees that you’re getting a happy, healthy pet.
Location: Tegus may cost more in places where supply is scarce or demand is higher.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of these animal prices:
- Hatchlings: $500-$700
- Juveniles: $700-$1,000
- Adults: $1,000-$2,000
- Rare Morphs: $2,000 or more
Are They Friendly?
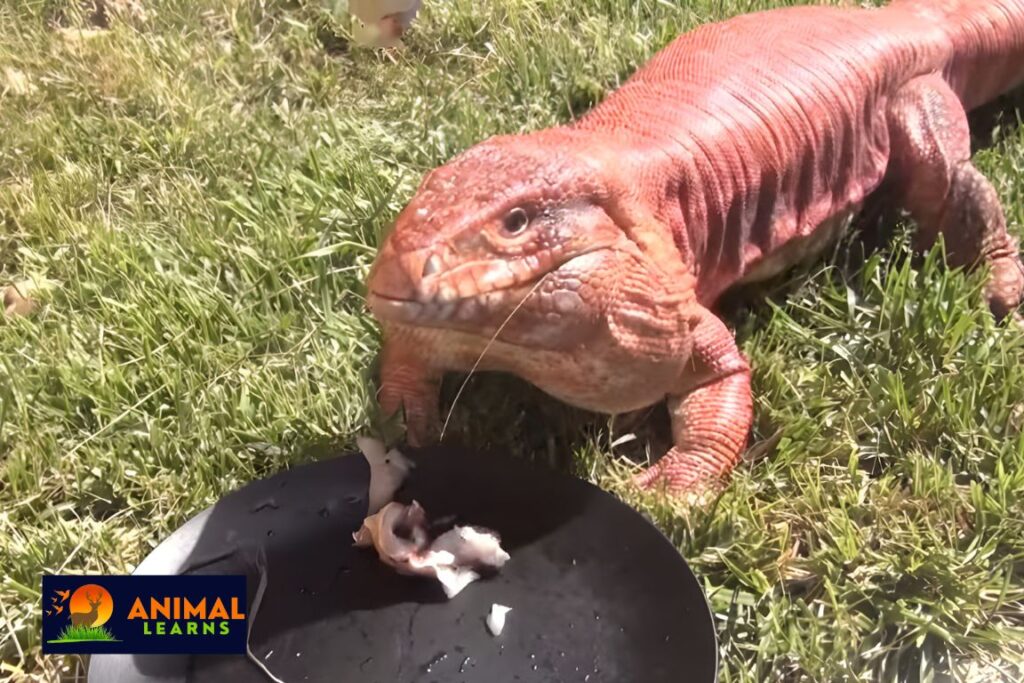

The fact that red reptiles are placid and easy to be around is one of their many appealing qualities. Additionally, there is hardly ever any hostility amongst cagemates.
Red tegu may grow to be quite huge, weighing up to fifteen pounds. It will constantly need you to handle it with additional caution. Your big person may be seriously hurt by just one drop. Tegus are so amiable that they may approach you for nibbles and rubs.
Always remember to fully wash your hands after handling anything since they may harbor bacteria that might be hazardous, such as salmonella.
Conclusion
If a red tegu sounds like the perfect pet for you, you might want to start looking for an exotic veterinarian in your area. Tegus are available nationwide at pet stores, or you may get them from a certified breeder with extensive knowledge of this species.
These animals require special care, so always make sure you have the time, space, and setup needed.
FAQs
Are Red Tegus good pets for beginners?
They are not recommended for beginners due to their size and specific care requirements.
What do Red Tegus eat?
They have an omnivorous diet, consuming a mix of vegetables, fruits, and high-quality protein sources like insects and small mammals.
How big does Red Tegus get?
They can grow quite large, with adult sizes ranging from four to over five feet, including their tail.
Are they aggressive?
While they can display aggression, proper socialization, and handling can result in docile behavior. Individual temperaments may vary.
What is the lifespan of Red Tegus?
With proper care, they can live for 15 to 20 years in captivity. Long-term commitment is essential when considering them as pets.












