Amazing Armadillos: Learn Their Mysteries

Armadillos are fascinating creatures. As a unique mammal, they can be found in various states, including Florida, Missouri, Kentucky, and Georgia. These animals are known for their distinctive habitat, often burrowing and creating intricate tunnel systems beneath the ground. One of the most intriguing aspects of armadillos is the sounds they make.
Some people are surprised to learn that armadillos can produce a variety of vocalizations, from squeaks to grunts, which adds an element of fun to their encounters.
Some people mistakenly believe that an armadillo is a type of rat, but in reality, they are unique and diverse creatures with a rich history and important ecological roles.
Appearance
Contents
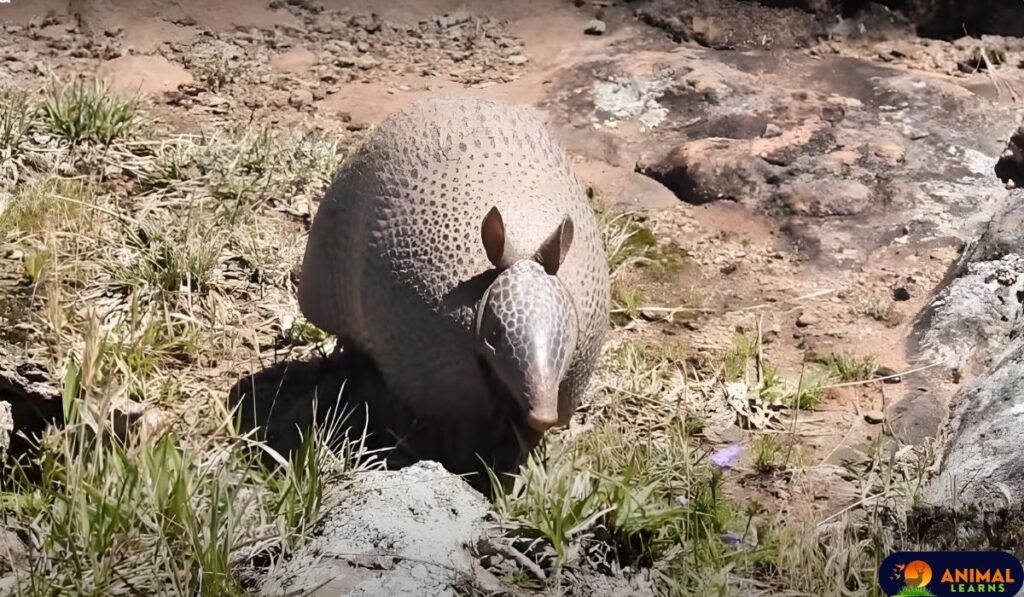

One of the most distinctive features of armadillos is their protective armor, made up of bony plates covered in tough skin. The armor acts as a shield, helping armadillos evade predators. Their shells vary in color, from gray to brown, and can have a leathery or scaly texture. Armadillos are relatively small mammals, with an average length of 6-24 inches (15-60 centimeters) and a weight that ranges from 3-120 pounds (1-54 kilograms), depending on the species.
Characteristics
- Armadillos are amazing animals with a unique armor-like exoskeleton that protects them from predators and injuries.
- They are expert diggers who can create elaborate underground homes with their sharp claws and strong limbs.
- They can swim across rivers and lakes with ease, despite their heavy shells, by inflating their lungs or sinking to the bottom.
- They enjoy a varied and nutritious diet of both plants and animals, such as insects, worms, small vertebrates, fruits, and sometimes dead animals.
- They can live for a long time in the wild, with some species reaching up to 15 years of age.
Diet
When it comes to armadillos’ food habits, they primarily feed on insects, making them valuable in controlling pest populations. Their favorite foods include ants and termites, and their lifespan varies depending on factors such as predation and habitat.
With their powerful sense of smell, they are skillful at detecting underground prey. Armadillos feed by digging small holes, probing their snouts into the soil to uncover insects, and utilizing their long sticky tongues to catch their prey.
Habitat and Distribution
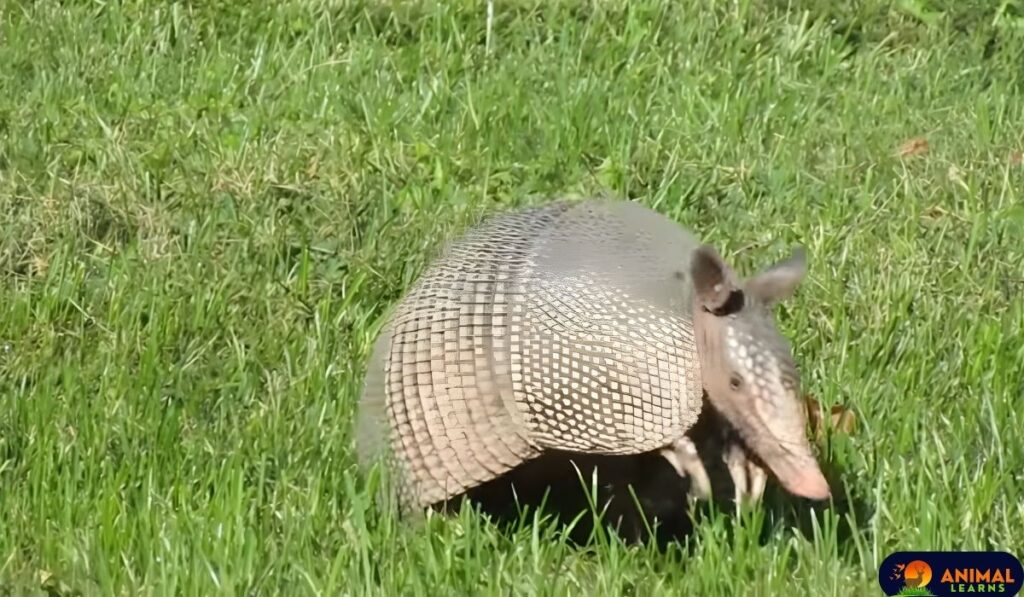

Armadillos inhabit various types of environments, ranging from grasslands and forests to deserts and wetlands. They are particularly abundant in Central and South America, with a few species extending into the southern part of the United States. In North America, the nine-banded armadillo is the most widely distributed species, found primarily in the southeastern region of the continent.
Behavior and Lifestyle
Many are curious about what armadillos do when they are seen digging holes in the yard, which is a common behavior as they search for their insect prey. While armadillos are not inherently dangerous to humans, they can carry diseases, which is one reason why they are sometimes kept as pets in certain regions. Armadillos are predominantly nocturnal animals, spending their nights foraging for food.
They are solitary creatures, only coming together for breeding purposes. Despite being excellent diggers, they do not build permanent burrows and instead create temporary diggings for shelter and protection. These burrows, which can be several meters long, serve as hiding places from predators and offer a comfortable environment to rest.
When confronted by predators, such as coyotes or foxes, armadillos rely on their shells for defense. They will quickly tuck their entire body into their shell, leaving only the tough armor exposed. If hiding is not an option, they have the ability to flee quickly and are strong swimmers in case they need to escape by water.
Types of Armadillos

The armadillo family consists of around 20 species, each exhibiting varying physical attributes and adaptations tailored to their specific environments. The most commonly known type is the nine-banded armadillo, scientifically referred to as Dasypus novemcinctus.
These armadillos are native to North and South America and are known for their impressive ability to roll themselves into a ball when threatened.
| Species Name | Color | Location | Size | Weight |
| Giant Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 39 inches | Up to 132 lbs |
| Southern Long-nosed Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 20 inches | Up to 4.4 lbs |
| Hairy Long-nosed Armadillo | Brown | South America | Up to 21 inches | Up to 5.5 lbs |
| Greater Fairy Armadillo | Pale yellow to pink | Argentina | Up to 5.5 inches | Up to 3.3 oz |
| Pink Fairy Armadillo | Pinkish-white | Argentina | Up to 4 inches | Up to 2.5 oz |
| Pichi | Grayish-brown | South America | Up to 8 inches | Up to 7.1 oz |
| Six-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 24 inches | Up to 8.8 lbs |
| Seven-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 24 inches | Up to 8.8 lbs |
| Nine-banded Armadillo | Brownish-gray | United States, Americas | Up to 24 inches | Up to 17 lbs |
| Northern Naked-tailed Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 10 inches | Up to 1.1 lbs |
| Southern Naked-tailed Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 10 inches | Up to 1.1 lbs |
| Big Hairy Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 26 inches | Up to 9.9 lbs |
| Andean Hairy Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 16 inches | Up to 3.3 lbs |
| Screaming Hairy Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 16 inches | Up to 3.3 lbs |
| Chacoan Naked-tailed Armadillo | Brownish-gray | South America | Up to 20 inches | Up to 3.3 lbs |
| Thick-tailed Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 21 inches | Up to 5.5 lbs |
| Three-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 14 inches | Up to 4.4 lbs |
| Brazilian Three-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 14 inches | Up to 4.4 lbs |
| Southern Three-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 14 inches | Up to 4.4 lbs |
| Bolivian Three-banded Armadillo | Yellowish-brown | South America | Up to 14 inches | Up to 4.4 lbs |
Interesting Facts about Armadillos
- Armadillos are remarkable reproducers who can deliver four identical babies at once, a rare and fascinating trait in the animal world.
- They are ancient animals with a long evolutionary history, dating back to over 60 million years ago when they shared ancestors with anteaters and sloths.
- They have poor vision but excellent smell and hearing, which help them find food and avoid danger, but also make them vulnerable to road accidents.
- They have unique and diverse armor patterns, ranging from nine bands to more or less, depending on the species and individual.
- They have left behind ancient fossils that reveal their past diversity, some of which resembled giant ground sloths and mammoths that roamed North America millions of years ago.
- They are one of the few animals that can contract and transmit leprosy, a disease that affects the skin and nerves, making them valuable for medical research.
- They vary greatly in size and appearance, from the tiny pink fairy armadillo that can fit in your hand, to the giant armadillo that can weigh up to 60 kg.
Population and Social Systems
Armadillo populations can be found throughout the Americas, with varying levels of abundance depending on the species and geographical region. They are most prevalent in grasslands, forests, and savannas.
Armadillos are primarily solitary creatures, with males and females coming together solely for mating purposes. They mark their territories using scent glands and generally prefer to inhabit areas with ample food supply and shelter.
Predators:
Despite their protective armor, armadillos are not entirely safe from predators. They have a few natural enemies that have adapted unique strategies to capture them. Some of the common predators include large birds of prey like eagles and owls as well as larger mammalian predators such as jaguars, cougars, wolves, and coyotes. Additionally, human activities, such as habitat destruction and hunting, contribute to the decline of certain armadillo species.
Mating and Reproduction

Armadillos have a peculiar reproductive system. Most species give birth to identical quadruplets, meaning all offspring are genetically identical, as they develop from a single fertilized egg. This characteristic is known as monozygotic polyembryony and is exceedingly rare among mammals.
The gestation period for armadillos is approximately 120 days, after which the young are born fully developed and ready to explore the world.
Challenges faced
- Habitat loss due to deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural activities
- Struggle to find adequate food sources, shelter, and breeding grounds
- Road mortality due to collisions with vehicles
- Impact on populations where road networks are dense
- Carrier of leprosy, a chronic infectious disease, poses a risk to both human and armadillo populations
- Concerns about disease transmission
- Climate change causing disruptions in the availability of food and water resources
- Impact on the timing of reproduction and migration
- Impact on survival and reproduction rates.
However, in the wild, armadillos are facing challenges, as some populations are endangered due to habitat loss and other factors. Learning more about where these creatures are found and understanding their role in the ecosystem is crucial for their conservation.
Additionally, the giant armadillo, a massive species of armadillo, is a significant focus of conservation efforts, as there are concerns about how many of these magnificent creatures are left in the world.
Conclusion
Armadillos are truly remarkable creatures, captivating the minds of both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. With their distinctive armor, impressive digging abilities, and diverse adaptations, these mammals have carved out a unique niche in the animal kingdom.
However, environmental alterations, hunting, and habitat destruction pose significant threats to their populations. As guardians of our planet, it is imperative to protect these fascinating creatures and ensure their survival for future generations.
FAQs
Is an armadillo a rat?
No, an armadillo is not a rat. Armadillos belong to a different family of mammals known for their unique armor-like shells.
What are armadillos used for?
Armadillos are not commonly used for any specific purpose. They are primarily wild animals and are not typically utilized in human activities.
What are 3 interesting facts about armadillos?
Three interesting facts about armadillos are their unique armor-like exoskeleton, their ability to give birth to identical quadruplets, and their surprisingly good swimming skills.
Are armadillos harmful?
Armadillos are generally not harmful to humans. However, they can carry diseases like leprosy, so caution should be exercised when handling them.
Are armadillos poisonous to humans?
Armadillos are not poisonous to humans. However, they may carry diseases, such as leprosy, which can be transmitted to humans through close contact, making it essential to handle them with care.